What Does A Vehicle Insurance Policy Cover And What Doesn’t It?
Vehicle insurance is a fundamental necessity for anyone owning or operating a motor vehicle. It offers financial protection against damages or losses arising from accidents, theft, or other unexpected events. However, insurance policies can be complex, filled with legal jargon and various clauses that may confuse policyholders about what is actually covered and what is not. Understanding these details is crucial to ensure you have adequate protection and avoid surprises when filing a claim.
In this comprehensive article, we will break down the components of a vehicle insurance policy, clearly outline what it covers, highlight exclusions, and answer the most frequently asked questions related to vehicle insurance.
Key Takeaways
- Vehicle insurance protects against financial losses due to accidents, theft, and third-party liabilities.
- Third-party insurance covers only damages caused to others; comprehensive insurance covers both third-party and own vehicle damage.
- Common exclusions include damage from negligence, wear and tear, intentional damage, and unauthorized use.
- Add-ons such as zero depreciation and engine protection enhance your coverage.
- Always verify policy terms, including geographical coverage and driver eligibility.
- Timely claim filing and accurate documentation are critical for smooth claim processing.
- Understanding your policy empowers you to choose the right coverage and avoid unexpected costs.
Understanding Vehicle Insurance Policy: The Basics
A vehicle insurance policy is a contract between you (the insured) and an insurance company (the insurer), wherein the insurer agrees to compensate you for certain types of losses related to your vehicle in exchange for premiums paid by you. This policy helps manage financial risks associated with accidents, damages, or theft.
Types of Vehicle Insurance Policies
- Third-Party Liability Insurance
This is the minimum legal requirement in many countries. It covers damages or injuries you cause to other people or their property. It does not cover damage to your own vehicle. - Comprehensive Insurance
This policy offers extensive coverage. It protects your vehicle against damage due to accidents, theft, natural disasters, vandalism, and more. It also includes third-party liability coverage. - Collision Insurance
Covers the cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle after a collision, regardless of who is at fault. - Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers after an accident. - Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Protects you if you’re in an accident with a driver who lacks adequate insurance.
What Does a Vehicle Insurance Policy Cover?
The scope of coverage depends largely on the type of insurance policy you hold and the specifics outlined in your contract. However, most vehicle insurance policies include the following core coverages:
1. Third-Party Liability Coverage
- Bodily Injury Liability:
Covers medical expenses, lost wages, and legal fees if you injure someone else in an accident. - Property Damage Liability:
Pays for damage to someone else’s property, such as their vehicle, building, or other assets.
2. Own Vehicle Damage Coverage
- Accidental Damage:
Covers repairs or replacement of your vehicle if it is damaged due to a collision or accident. - Theft or Vandalism:
Protects against loss if your vehicle is stolen or deliberately damaged. - Natural Calamities:
Includes damages due to floods, storms, earthquakes, hailstorms, landslides, and other natural disasters. - Fire Damage:
Covers damages due to fire or explosion involving your vehicle.
3. Medical Expenses
- Medical costs for you and your passengers due to injuries sustained in a vehicle accident.
4. Personal Accident Cover
- Provides compensation in case of death or permanent disability of the driver or insured due to a road accident.
5. Emergency Roadside Assistance
- Some policies include roadside assistance services such as towing, battery jump-start, flat tire change, or fuel delivery.
6. Loss of Use / Rental Reimbursement
- Covers the cost of renting a vehicle while your insured vehicle is being repaired due to an accident or covered event.
What Does a Vehicle Insurance Policy NOT Cover? — An In-Depth Analysis
Vehicle insurance policies are designed to provide financial protection against a wide range of risks associated with operating a motor vehicle. However, insurers clearly outline certain exclusions — specific scenarios or types of damages for which they will not provide compensation. These exclusions are fundamental to the insurance contract because they protect insurers from excessive or unfair risks and ensure policyholders maintain responsible use of their vehicles.
Let’s explore these exclusions in depth, understanding the rationale behind them and their practical implications for vehicle owners.
1. Damage Due to Driver Negligence
Explanation:
Insurance companies generally exclude coverage for damages caused by negligent or illegal driving behavior. This includes:
- Reckless driving: Excessive speeding, dangerous overtaking, ignoring traffic signals.
- Driving under the influence: Operating the vehicle while intoxicated by alcohol or drugs.
- Driving without a valid license: Operating the vehicle without a legally recognized driver’s license.
Why is it excluded?
- These behaviors significantly increase the risk of accidents and losses.
- Allowing claims for such negligence would encourage irresponsible driving.
- Most legal systems penalize such conduct, and insurers reflect this risk in their policies by excluding coverage.
Practical implications:
If you cause an accident while intoxicated or without a license, your insurer will likely deny the claim, leaving you personally liable for all damages and legal consequences.
2. Wear and Tear
Explanation:
Insurance policies do not cover damages that result from normal wear and tear or mechanical breakdowns. This includes:
- Gradual deterioration of tires, brakes, engine parts, and other mechanical components.
- Rust, corrosion, or any damage caused by aging.
- Failures caused by lack of maintenance or poor upkeep.
Why is it excluded?
- Wear and tear is considered a natural and expected process of vehicle usage.
- Insurance is meant to cover sudden, accidental losses, not predictable maintenance costs.
- Covering wear and tear would turn insurance into a vehicle maintenance service, which is not financially sustainable.
Practical implications:
You are responsible for regular servicing and maintenance of your vehicle. Insurance only kicks in when an unexpected accident or event causes damage.
3. Intentional Damage
Explanation:
Damage caused deliberately by the policyholder or someone acting with their consent is not covered.
Why is it excluded?
- Insurance contracts are based on the principle of indemnity, which means compensation for accidental losses, not intentional ones.
- Covering intentional damage would encourage fraudulent claims and moral hazard, where insured parties might purposely damage their vehicle for a payout.
Practical implications:
If an insurer suspects that damage was self-inflicted, the claim will be denied and may lead to cancellation of the policy or legal action.
4. Using Vehicle for Unauthorized Purposes
Explanation:
If you use your vehicle for purposes other than those declared in the insurance policy, claims may be denied. Common unauthorized uses include:
- Using a private-use insured vehicle for commercial purposes like ride-sharing or goods delivery.
- Using the vehicle in racing, stunt driving, or other high-risk activities not covered by the policy.
Why is it excluded?
- Different types of vehicle use carry different risk profiles.
- Commercial use involves higher liability and wear, so insurers require separate policies.
- Unauthorized use misrepresents the risk assumed by the insurer.
Practical implications:
If an accident occurs while your vehicle is being used commercially but is insured as private, the insurer can deny the claim, leaving you financially exposed.
5. Uninsured Modifications
Explanation:
Damage caused or aggravated by unauthorized or non-approved modifications to your vehicle may not be covered. Examples include:
- Engine tuning or performance upgrades.
- Alterations affecting safety systems like brakes or airbags.
- Installing non-approved body kits or accessories.
Why is it excluded?
- Modifications can significantly alter the vehicle’s risk profile.
- Unauthorized mods might void manufacturer warranties and compromise safety.
- Insurers are not liable for damages resulting from unapproved changes they did not assess.
Practical implications:
Always disclose modifications to your insurer. Failure to do so may result in claim denial or policy cancellation.
6. Damage to Non-Insured Parts and Personal Belongings
Explanation:
Most vehicle insurance policies cover the vehicle itself but exclude personal belongings inside the vehicle such as:
- Electronics, bags, clothing, or any items stored inside.
- Damage to items carried in the vehicle not listed explicitly in the policy.
Why is it excluded?
- Personal belongings are usually covered under homeowners or renters insurance, not vehicle insurance.
- Covering these items would complicate claims and increase premiums.
Practical implications:
Consider separate insurance for valuable personal items or ensure your home insurance includes coverage for possessions outside your residence.
7. Acts of War, Terrorism, or Nuclear Damage
Explanation:
Damage resulting from extraordinary events like:
- War, invasion, rebellion, terrorism.
- Nuclear reaction, radiation, or radioactive contamination.
These are almost universally excluded.
Why is it excluded?
- These events are considered catastrophic and outside normal insurance risk pools.
- Losses from such events are typically covered by specialized government programs or reinsurance schemes.
Practical implications:
While rare, these exclusions mean your insurance won’t cover damage from extreme geopolitical or environmental catastrophes.
8. Driving Outside Policy Territory
Explanation:
Vehicle insurance policies specify the geographical limits (territory) where coverage applies. Driving outside this area typically voids coverage.
Why is it excluded?
- Insurers base premiums on risks within specific regions or countries.
- Traffic laws, claim processes, and risk profiles vary widely by geography.
- Driving outside the specified territory introduces unassessed risks.
Practical implications:
If you plan to take your vehicle abroad, check your policy or arrange for additional coverage or green cards to ensure you are protected.
Additional Optional Coverages and Riders
Many insurers offer add-ons or riders to enhance your vehicle insurance coverage:
- Zero Depreciation Cover:
Pays full cost of replaced parts without depreciation deduction. - Engine and Gearbox Protection:
Covers repairs to critical mechanical components. - No Claim Bonus (NCB) Protection:
Allows you to retain your no claim bonus even after making a claim. - Key Replacement Cover:
Covers the cost of lost or stolen vehicle keys.
Factors Affecting Vehicle Insurance Coverage
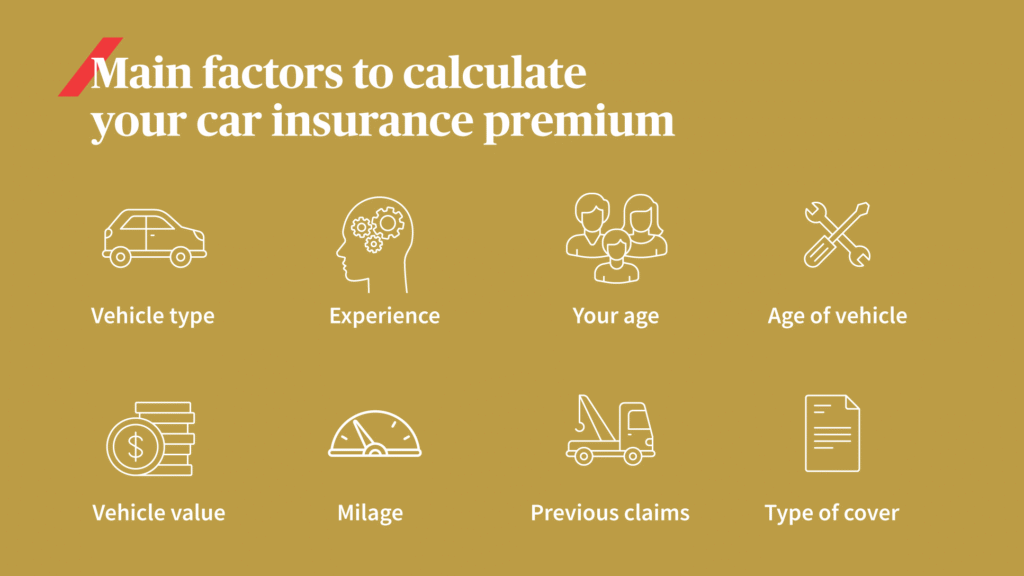
Several factors influence the scope, cost, and limitations of your vehicle insurance coverage:
- Type and Age of Vehicle
- Location of Vehicle Use
- Driving History of Policyholder
- Coverage Limits and Deductibles
- Add-ons and Riders Selected
Also Read:- What’s the Best Car Insurance for Your Needs?
Conclusion
A vehicle insurance policy is a vital financial tool that safeguards you against significant monetary losses arising from accidents, theft, or other unfortunate events involving your vehicle. Understanding what your policy covers—and just as importantly, what it does not—is essential to avoid surprises during claim settlement. While third-party liability insurance is the legal minimum, comprehensive insurance offers more extensive protection and peace of mind.
Always read your policy document carefully, ask your insurer for clarifications, and consider adding optional coverages to suit your specific needs. This way, you ensure that your vehicle and your financial interests remain well protected on the road.
Also Read:-
FAQs
1. Is vehicle insurance mandatory?
Yes, in most countries, third-party liability insurance is legally mandatory to protect other road users from damage caused by your vehicle.
2. What is the difference between third-party and comprehensive insurance?
Third-party insurance covers only damage or injury you cause to others. Comprehensive insurance covers both third-party liabilities and damage to your own vehicle.
3. Does insurance cover damages due to natural disasters?
Comprehensive insurance policies usually cover damages caused by natural calamities such as floods, storms, or earthquakes.
4. Are personal belongings inside the car covered?
No, most vehicle insurance policies do not cover personal belongings inside the vehicle unless specified in an add-on.
5. What happens if I drive without a valid license?
Most insurance policies will deny claims arising from accidents caused while driving without a valid license.
6. Can I insure a leased or rented vehicle?
Yes, you can insure leased or rented vehicles. Sometimes the leasing company may have insurance, but it’s advisable to confirm coverage details.
7. How do I file a claim after an accident?
Report the accident to the insurance company promptly, submit required documents such as a police report, photos, and repair bills, and follow the insurer’s claims process.
